|
| |
TM 9-254
7-3.
Alternating Current - Continued
c.
AC Power. The power expended in an AC circuit is calculated by the formulas:
NOTE
The phase angle q is the difference in degrees that the current leads or lags the voltage in a
reactive circuit. The phase angle is determined by the formula:
q = arctan
X
R
Where:
X is the inductive or capacitive reactance in ohms.
R is the resistance in ohms.
P = I2Z cos q
P = IE cos q
P = E2 cos q
Z
Where:
P is the power in watts.
E is the voltage in volts.
I is the current in amperes.
Z is the impedance in ohms.
q is the phase angle in degrees.
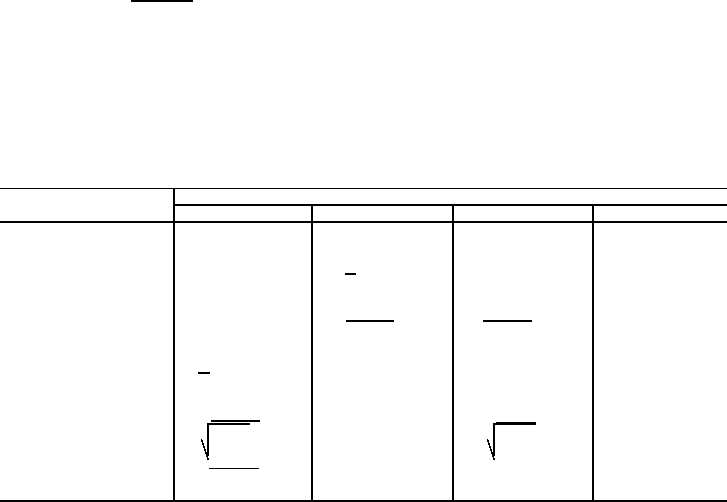
Table 7-2 shows the basic voltage, current, and power relationships for AC circuits.
Table 7-2. AC Relationships
Known
Formulas for determining unknown values of
values
I
R
E
P
I & Z
-
-
E = IZ
P = I2Z cos q
I & E
-
Z = E
I
-
P = IE cos q
I & P
-
Z =
P
I2 cos q
E =
P
I cos q
-
Z & E
I =E
Z
-
-
P = E2 cos q
Z
Z & P
I =
P
Z cos q
-
E =
PZ
cos q
E & P
I =
P
E cos q
Z = E2 cos q
P
-
-
7-5
|