|
| |
TM 9-254
7-3.
Alternating Current.
a.
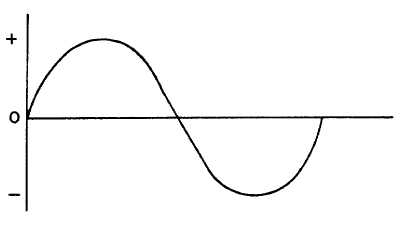
General. Alternating current or AC consists of the flow of electrons in first one direction and then in the
opposite (alternate) direction in a closed circuit. Typical AC such as household current switches direction in a cyclic
manner as shown by the sine wave in figure 7-4.
Figure 7-4. AC Sine Wave
b.
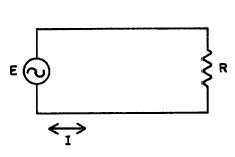
Ohm’s Law for AC Circuits. The difference between Ohm’s Law for DC and Ohm’s Law for AC is the
resistance (R) has been replaced by the impedance (Z). Ohm’s Law states that the current flowing in an AC circuit is
directly proportional to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to the circuit impedance. Figure 7-5 shows a simple
AC circuit and the various forms of Ohm’s Law which apply to AC circuits.
I =
E
Z
E = IZ
E =
E
I
Where:
E is the voltage in volts.
I is the current in amperes.
Z is the impedance in ohms.
Figure 7-5. Ohm’s Law for AC Circuits
7-4
|