|
| |
TRUCK SERVICE MANUAL
TM 5-4210-230-14&P-1
FUEL SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
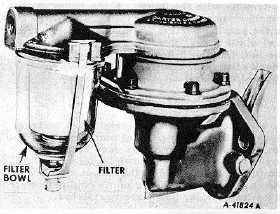
The fuel pumps used on most gasoline type engines
are of the mechanical type and are mounted on the engine,
Fig. 1. The suction side of the pump is connected to the fuel
tank and the discharge side is connected to the carburetor by
tubing designed to carry the fuel. The purpose of the pump
used on gasoline type engines is to suck fuel from the supply
tank and push it into the carburetor float bowl as required by
the engine.
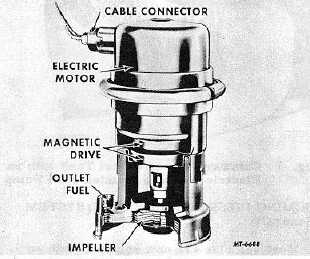
Electric fuel pumps are also used to supply the fuel
from the tank to the engine. In most cases the electric fuel
pump is located in the fuel tank, Fig. 2.
Fig. 1 Mechanical Fuel Pump (Side Mounted Bowl Type)
Fig. 2 In-Tank Mounted Electric Fuel Pump
OPERATION
Mechanical Fuel Pump
In general the pumping operation for all mechanical
pumps is accomplished through a pump rocker arm which
contacts a special cam on the engine camshaft. The rocker
arm in turn actuates a diaphragm in the pump, and this
action, together with the action of inlet and outlet valves in the
pump, causes gasoline to flow through the pump. Pumping
action is controlled, however, by fuel pressure in the pump
outlet line. When the float needle valve in the carburetor is
not seated and the fuel passage into the carburetor float
chamber is open, gasoline will flow to the carburetor. When
the needle valve is closed and held in place by the pressure of
the fuel in the bowl and on the float, the pump will continue to
build up pressure until it overcomes the pressure of the pump
diaphragm spring. This pressure results in almost complete
stoppage of diaphragm movement until further fuel is needed.
Electric Fuel Pump (In-Tank Mounted)
The in-tank mounted electric fuel pump is cushioned
in neoprene to dampen vibrations and is supported by an
adjustable hanger assembly, which makes it adaptable to all
IH fuel tank depths. A spring-loaded latch permits easy motor
replacement. Electrical connections are the sealed quick-
disconnect type, Fig. 2.
MAINTENANCE
Efficient operation of the fuel pump depends on the
proper maintenance of the fuel filter. For this reason the filter
should be checked from time to time to note any accumulation
of dirt, water, or other foreign objects. The interval for actual
cleaning or replacing of the filter element is dependent on
engine operating conditions.
Engines which are equipped with in-tank mounted
electric fuel pump are either equipped with one or two fuel
filters in the system, depending upon the type of engine.
Gasoline type engines are equipped with an in-line fuel filter.
A primary and secondary fuel filter are both used on diesel
engine applications. The primary filter is the first filter in the
line from the fuel tank. The secondary fuel filter is usually
located on the engine.
To clean the wire screen: disc type filter, remove the
filter bowl and filter and wash these parts in a commercial
carburetor clean-
CTS-2050-F
Page 3
PRINTED IN UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
|