|
| |
TRUCK SERVICE MANUAL
TM 5-4210-230-14&P-1
Fig. 2 Maintenance Free Type Battery
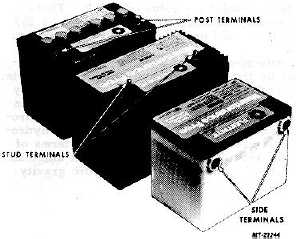
Batteries are provided with side, top stud and top post type
terminals (Figure 3) for various vehicle applications.
LOW MAINTENANCE BATTERIES
These are conventional lead-acid batteries requiring normal
periodic battery maintenance.
A small amount of antimony has been added to the lead to
improve grid strength. The antimony tends to cause "gassing"
(breaking down of water into hydrogen and oxygen gases)
during battery operation, thereby lowering the electrolyte level.
Hence, periodic addition of water to the battery cells is
required.
"Fleetrite" and "International" batteries are provided with easily
accessible cell filler caps.
MAINTENANCE FREE BATTERIES
Maintenance free batteries do not require the addition of water
during normal service life. This is due to the fact that
maintenance free batteries utilize calcium rather than
antimony to improve grid strength. The advantage of calcium
is that it greatly reduces the tendency for the battery to gas at
normal charging voltages. Consequently, very little water is
used.
Maintenance free batteries are not sealed. All batteries
(including
maintenance-free)
generate
gases,
especially
during charge. While the volume of gases produced by the
maintenance free battery is reduced by more than 75%, there
are small vent openings to allow this gas to
Fig. 3 Types of Battery Terminals
escape. The corrosive sulfuric acid mixture will escape if the
battery is turned upside down or placed on its side.
"Fleetrite" and "International" maintenance free batteries have
concealed cell caps which can be removed to permit battery
testing and addition of water if required.
ELECTROLYTE AND SPECIFIC GRAVITY
The electrolyte in a lead-acid storage battery is a dilute
sulfuric acid solution. The sulfuric acid in the electrolyte is
one of the necessary ingredients in the chemical actions
taking place inside the battery. It supplies the sulfate which
combines with the active material of the plates. It is also the
carrier for the electric current as it passes from plate to plate.
When the battery terminals are connected to an external load,
the sulfate combine's with the active materials of the positive
and negative plates forming lead sulfate and releasing
electrical energy. Electrons flow from the negative terminal to
the load (such as headlamps), and back to the positive
terminal.
SPECIFIC GRAVITY
Specific gravity is a unit of measurement for determining the
sulfuric acid content of, the electrolyte. The recommended
fully charged specific gravity of most 12-volt batteries today is
1.265 corrected to 26.7° C (80° F). A battery with a fully
charged specific gravity of 1.265 contains an electrolyte with
approximately 36% sulfuric acid by weight or 25% by volume.
The remainder of the electrolyte is water. Pure (concentrated)
sulfuric acid has
CTS-2771 Page 5
PRINTED IN UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
|