|
| |
TRUCK SERVICE MANUAL
TM 5-4210-230-14&P-1
BRAKES-HYDRAULIC
The terms micrometres, micro-inch or surface finish
or smoothness are different from runout and parallelism.
These terms refer to degree of how smooth the flat surface is.
However, if good, sharp tools and proper cutting feed and
speed are used when remachining the rotor, you should be
within
the
.381-2.032
micrometres
(15-80
micro-inch)
tolerances.
INSPECTION OF PADS
The disc brake pads or shoes can be inspected for
wear on the vehicle. It is normal for the inboard lining to show
more wear than the out board lining. Always install new pads
assemblies in complete axle sets at both wheels on an axle.
Since lining on disc brakes will be bonded (code
04135) and riveted (codes 04138, 04139 & 04140) the
useable thicknesses will be different.
Pads with bonded lining (code 04135) must be
replaced when lining is worn to .7937 mm (1/32 in.) or less.
Pads with riveted lining (codes 04138, 04139 &
04140) must be replaced when lining is worn to 3.1750-
4.7625 mm (1/8 to 3/16 in.) or less.
It is suggested that the pads be replaced whenever
they are removed for an inspection or for any other service
and they are found to be worn to 2.778 mm (7/64 in.) from
shoe surface with bonded material, or from rivet heads to
brake lining surface.
DRUM REPLACEMENT
Different assembly methods are used to hold brake
drums in their piloted position on hub while wheels are
dismounted.
LIGHT DUTY VEHICLES
Drums which are mounted against wheel flange on
light duty vehicles are secured to studs either with speed nut
fasteners or by swagging the piloting shoulder of stud to
drum. To replace an original drum proceed as follows:
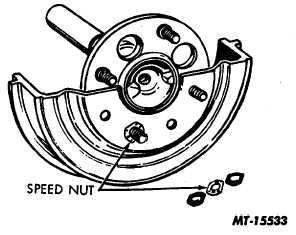
Where threaded fasteners (Fig. 20) are used simply
unthread speed nuts and lift drum from flange.
Fig. 20 Threaded Fastener Type Drum Mounting
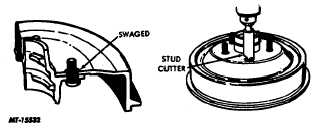
If swaged stud mounting (Fig. 21) is used, chuck a
stud cutter in an electric drill, align cutter over each stud and
cut away the swaged material. Separate drum from hub and
discard drum.
Fig. 21 Swaged Stud Type Drum Mounting
MEDIUM AND HEAVY DUTY VEHICLES
Drum replacement on medium and heavy duty
vehicles requires the removal of nuts from bolts securing hub
and drum together. The hub and drum can then be
separated.
MOUNTING NEW DRUM TO HUB
Clean exposed hub or axle mounting flange with wire
brush or coarse file. Use straight edge across surface of
flange to make sure it is not bent. Remove excess paint from
edge of drum hub hole and wash rust preventive sealer from
drum with solvent.
CTS-2779 Page 9
PRINTED IN UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
|