|
| |
TRUCK SERVICE MANUAL
TM 5-4210-230-14&P-1
DESCRIPTION
The various axles contained in this section are full floating,
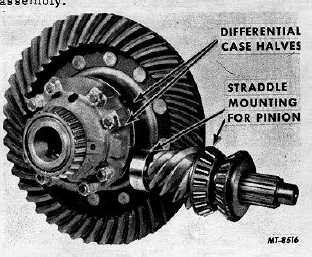
single reduction units. Fig. 1 illustrates the single reduction
differential assembly.
Fig. 1 Differential Assembly
The construction of rear axles may vary as to design, but the
fundamental components of the axles perform similarly
regardless of the type. The basic parts of the axle with which
the serviceman will be concerned are the drive gears, the
differential assembly, the axle shafts, and the housing.
MAINTENANCE
Lubrication
The most important item of axle maintenance about which the
truck operator must be concerned is lubrication. For this
reason factory recommendations on lubrication intervals,
methods of filling, lubricant levels, draining and type of
lubricant must be followed to assure long life and satisfactory
performance. Inspect the axle frequently for lubricant
leakage, especially around housing covers, pinion oil seal
retainer and axle shaft flanges. When necessary, change
gaskets or seals and keep nuts or bolts tight. See
"Lubrication" section in the Operator's Manual provided with
each truck.
Axle Housing Breather Valve
To prevent a pressure build-up in the axle housing when the'
axle becomes warm after a short period of operation, a
breather valve, Fig. 2, is provided in rear axles. Without this
valve the resulting pressure could force the axle lubricant past
the rear wheel oil seals and
damage the brake linings. The valve is so constructed that
warm air may pass out of the axle to relieve built-up pressure,
yet dirt and moisture are prevented from entering.
The breather valve should be kept open and clean. When the
truck is operated off highway on unimproved roads or in ice
and snow, dirt may sometimes be forced under the valve cap
and cause the valve to become ineffective. Remove valve
occasionally and clean thoroughly in a cleaning solution.
Fig. 2 Location of Breather Valve in Axle Housing
Alignment
The rear axle should also be checked at regular intervals to
determine if there is any misalignment of the axle with frame
or drive line. Evidence of misalignment may sometimes be
noted at the U-bolts. To check for axle misalignment, lay a
straightedge across and at right angles to the truck frame.
The straightedge should be longer than the axle tread and
clamped to the frame a short distance ahead of the rear axle.
Measure the distance between the straightedge and identical
points at each end of the axle assembly. When distances are
not equal, misalignment is indicated, and rear springs and U-
bolts must be checked for correct assembly.
Drive Gears
These IH rear axles have the hypoid type of drive as illustrated
in Fig. 3.
Because of the offset type of construction,
CTS-2095S-CHAPTER I-Page 3
PRINTED IN UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
|