|
| |
TM 9-254
7-4.
Resistor Identification - Continued
d.
Resistor Voltage/Wattage Rating. Another important factor in resistor selection/identification is the
voltage/wattage rating of the resistor. This rating is an indication of the maximum amount of power the resistor is capable
of handling. The following paragraphs explain several methods used.
(1)
On variable resistors and some fixed resistors the voltage and or wattage rating will be indicated by
numbers and letters printed on the resistor.
(2)
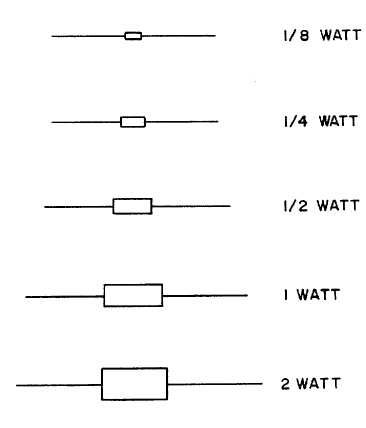
In the case of color coded carbon composition resistors, the wattage is normally indicated by the size
(length and diameter) of the resistor. The smaller the size of a resistor, the less power or voltage it can
handle. Typical wattage sizes are 1/8, 1/4, 1/2, 1, and 2 watts. Figure 7-10 can be used as a quick
reference in determining the wattage of this type resistor. Larger wattage resistors are typically wire-
wound and they will have their wattage printed on their side.
Figure 7-10. Typical Carbon Resistor Wattage Reference Chart
7-5.
Capacitor Identification.
As is the case with resistors there are many types and sizes of capacitors and many ways of marking them. Figure 7-11
shows many of the different types of capacitors and marking systems which may be encountered. One type of capacitor
not shown in figure 7-11 is the electrolytic capacitor. This type capacitor comes in many shapes and sizes. DC electrolytic
capacitors have their positive terminal marked and care must be taken to insert them into the circuit properly. The
capacitance and voltage rating of this type capacitor is typically printed on the side of the capacitor.
7-10
|