|
| |
TM 9-254
7-3.
Alternating Current - Continued
(a)
For parallel circuits:
RX
Z =
R2 + X2
(b)
For series circuits:
Z =
R2 + X2
Where:
Z is the total impedance in ohms.
R is the total resistance in ohms.
X is the total reactance in ohms.
e.
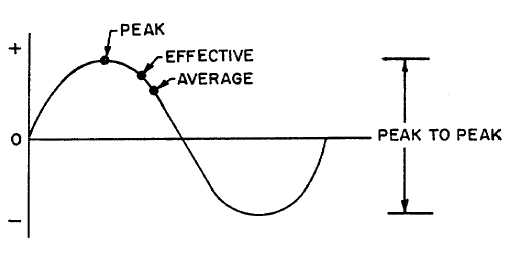
Instantaneous Values of AC Voltage. As the AC voltage and current pass through the sine wave cycle
depicted in figure 7-8, there are several instantaneous values of interest, such as the peak, effective, and average values
of the sine wave.
Figure 7-8. Instantaneous Values of AC
The relationships between the instantaneous values shown are provided in table 7-3. Given any one of the four values,
the remaining three values can be calculated using the relationships from the table.
Table 7-3. Instantaneous Values of AC
Given
Multiplying factor to get
Values
Average
Effective
Peak
Peak-to-Peak
Average
-
1.11
1.57
3.14
Effective
0.9
-
1.414
2.828
Peak
0.637
0.707
-
2.0
Peak-to-Peak
0.32
0.3535
0.5
-
7-8
|