|
| |
ENGINE DIVISION SERVICE MANUAL
TM 5-4210-230-14&P-1
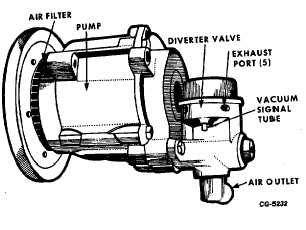
Fig. 71 Air Injection Pump With Diverter Valve
(Except California)
(1)
Disconnect left bank air injection hose from air
manifold check valve and connect air pump output
tester SE-2498 to end of hose.
(2)
Disconnect left bank pressure limiting hose from air
cleaner and plug end of hose.
(3)
Connect tachometer to engine.
(4)
Operate engine at speed specified (see Emission
Control Tune-Up Specifications)
(5)
Observe pressure indicated. If air pressure does not
exceed minimum specification (see Emission Control
Tune-Up Specifications) perform the following steps
a, b, c and d.
a.
Check air hoses for leaks. Check diverter
valve for, external leaks. If leaks are found,
replace hose(s) and/or diameter valve and
repeat steps 4 and 5.
b.
Disconnect air hose (connecting air pump
outlet to diverter valve inlet) from diverter
valve and connect air pump output tester SE-
2498 to end of hose.
c.
Operate engine at specified speed (see
Emission
Control
System
Tune-Up
Specifications)
and
observe
minimum
pressure.
(1)
If air pressure is less than specified minimum (see
Emission Control System Tune-Up Specifications),
air pump is faulty and must be replaced. When
installing a new air pump or adjusting the air pump
belt tension, do not pry on the pump housing.
(2)
If air pump pressure is higher than specified
minimum (see Emission Control System Tune-Up
Specifications), diverter valve is faulty and must be
replaced.
d.
Connect air pump output tester SE-2498 to air
injection hose removed from check valve.
Connect air injection hose from air pump to
diverter valve inlet and repeat steps 4 and 5.
(6)
With the engine operating at speed specified,
observe the pressure gauge. Multiply observed
pressure by .7 to obtain multiplied pressure.
(Example: Observed pressure is 6 PSI and multiply
by .7. 6 x .7 = 4.2 PSI multiplied pressure)
(7)
Remove plug in the pressure limiting hose and
observe the pressure gauge.
a.
If observed pressure in step 7 is higher than
multiplied pressure in step 6, diverter valve is
acceptable for further use.
b.
If observed pressure in step 7 is lower than
multiplied pressure in step 6, diverter valve is
faulty and must be replaced.
(8)
With the engine operating at speed specified (see
Emission Control System Tune-Up Specifications),
remove vacuum hose from diverter valve and check
for vacuum pull at the end of the hose. If no vacuum
is felt, check for restriction in vacuum hose, vacuum
manifold and carburetor vacuum port. Repair as
needed.
CGES-215 Page 41
PRINTED IN UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
|