|
| |
TRUCK SERVICE MANUAL
TM 5-4210-230-14&P-1
WHEELS, RIMS, TIRES
TIRE INJURIES
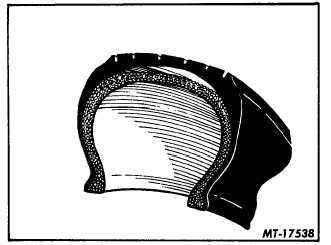
Ply or Tread Separation:
Ply or tread separation as shown in Fig. 18 can result
from underinflation, overloading, or high speed.
Driving a tire that is flat or seriously underinflated can
cause unrepairable cord breakage, ply, and even tread
separation. The amount of damage is directly proportional to
the amount of underinflation and distance driven in this
condition.
Fig. 18 Tread Separation Result of Underinflation, Overloading,
or High Speed
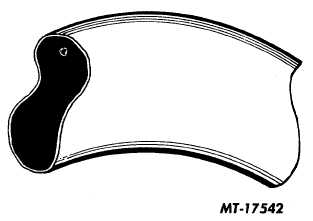
Cord Breakage:
The proper deflection of tire sidewalls is inhibited by the
increased tension caused by overinflation. Overinflation
increases strain on the cords in the tread area and the tire loses
its ability to absorb ordinary road shocks. Under this
overinflated condition an impact can cause either an X-break or
a diagonal break. Four pounds extra pressure for high speed
driving is not considered overinflation, providing the maximum
inflation of the tire is not exceeded. Reduce cool air pressure to
recommended level. Never "bleed" air from a hot tire.
Even with properly inflated tires, cords can be broken
when a tire is crushed between an object like a concrete curb
and steel rim of the wheel. The position and breakage of cords
is determined by the angle and force of impact.
Fig. 19 Broken Cords Caused by Severe Blow
INNERTUBE INJURIES
Chafed Innertube:
Innertubes that are chafed by the tire can be prevented
by proper mounting techniques. First inflate innertube to 10 psi,
deflate and reinflate innertube to recommended pressure. This
procedure will prevent chafing.
Damage to both the innertube and inside of tire can be
caused by not cleaning foreign matter from tire, innertube, or
wheel at time of assembly. Thoroughly clean tire, innertube,
and wheel removing all foreign matter, dirt, rust, and labels
from all surfaces.
Fig. 20 Damage Caused by Dirt In Tire
CTS-2176N Page 9
PRINTED IN UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
|