|
| |
TM 9-254
7-12.
Troubleshooting with the Technical Manual - Continued
(3)
Do the checkout procedure in Volume I, Chapter 2 from the beginning until you find a fault symptom.
(4)
When a fault symptom is found, go to the chapter noted and follow the maintenance procedure given
there. If you already know the fault symptom, look at the fault symptom index in Chapter 3 of this
volume.
(5)
After the bad part has been repaired or replaced, do the checkout procedure in Chapter 2 again. This is
to make sure all fault symptoms have been corrected.
(6)
If all the faults are now corrected, do the remaining maintenance tasks on DA Form 2404.
(7)
Do the final inspection given in Volume II, Chapter 5.
(8)
The job is over and the good assembly is sent back to service.
(9)
If all faults were not corrected after step 5, the bad assembly is sent to the depot for repair.
7-13.
Half-Split Method of Troubleshooting.
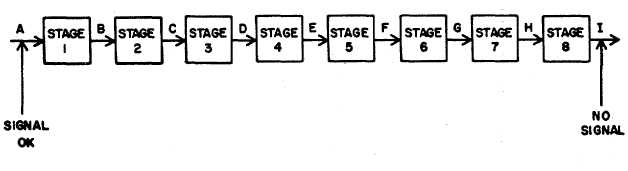
Half-splitting is a technique used in trouble shooting which reduces the average number of measurements needed to
isolate the faulty stage or component. Consider the eight stage path shown in figure 7-21 and the technique explained in
the following paragraphs
Figure 7-21. Eight Stage Block Diagram
(1)
The first measurement using half-splitting would be made at point E (the middle of the faulty path). If the
signal is okay at point E the path to the left of point E is good and the problem lies between points E and
I. Thus one measurement has reduced the size of the faulty path by one-half (half-splitting).
(2)
The next measurement would be made at point G again splitting the faulty path in half. If the
measurement at point G is bad (no signal) the next measurement would be made at point F. This
method of splitting a faulty path in half is continued until the faulty stage is isolated.
7-24
|